What is Core Muscles?
Core muscles is the central part of the body. Core muscles is a group of trunk and hip muscles which surround the spine, abdominal viscera and hip. During activities of daily living, core muscles play a vital role in proper load balance.

Importance of core activation
Enhanced Stability and Posture:
- Spinal Support: Your core muscles, including the deep stabilizing muscles like the transverse abdominis and multifidus, work together to support your spine. This support is crucial for maintaining proper posture and reducing the risk of back pain or injury.
- Pelvic Alignment: Core activation helps in stabilizing the pelvis, promoting proper alignment. This alignment not only prevents issues like lower back pain but also ensures that weight is evenly distributed, reducing strain on different parts of the body.
Improved Functional Movement:
- Efficiency in Movements: A strong core allows for more efficient transfer of energy between the upper and lower body. This efficiency is crucial for everyday activities, from lifting groceries to picking up a child. By engaging your core, you’re ensuring that these movements are executed more safely and effectively.
- Balance and Coordination: Core activation enhances balance and coordination by improving proprioception—the body’s ability to sense its position in space. This is beneficial not only in sports but also in daily activities, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
Optimized Athletic Performance:
- Force Generation: Athletes rely on their core strength for generating power and force. From explosive movements like sprinting and jumping to the controlled rotation needed in sports like baseball or martial arts, a strong core maximizes the efficiency and effectiveness of these movements.
- Injury Prevention: For athletes, a strong core not only improves performance but also reduces the risk of injuries. It acts as a shield, absorbing impact forces and providing stability during rapid movements, thereby lowering the chance of strains or sprains.
How to activate the core muscle?
- Sitting
- Sit on a chair (put a mirror in front of you )
- Push the abdominal muscles out without holding the breath (imaging there is somebody going to punch your tummy)
- Followed by push the lower back muscles out without holding the breath
- Contract the pelvic floor muscles
- Adjust the pelvic bone to make it in a neutral position (avoid pelvic bone move forwardly or backwardly)
- Stay elongated
- Slowly move the body forward and try to stand up
- Sit down again and repeat for all the steps 10x

2.Standing
- Stand in front of a mirror if allowed
- Unlock both knees
- Turn both knees out without moving the feet
- Adjust the pelvic bone to make it in a neutral position (avoid pelvic bone move forwardly or backwardly)
- Shoulder relax
- Push the abdominal muscles out without holding the breath (imaging there is somebody going to punch your tummy)
- Followed by push the lower back muscles out without holding the breath
- Contract the pelvic floor muscles
- Stay elongated
- Maintain the posture for 2 minutes
- Repeat 10 times
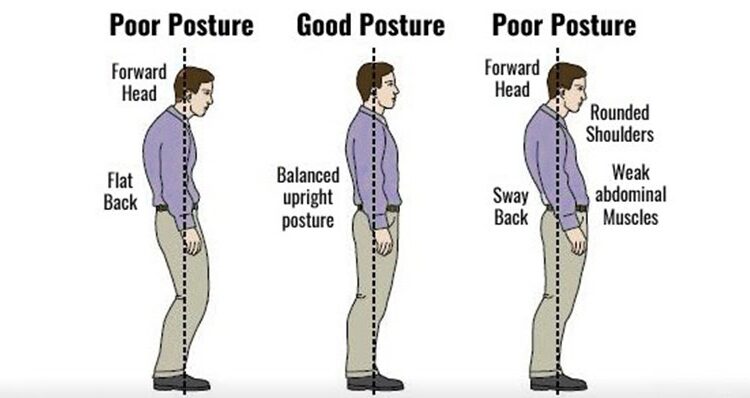
In essence, the activation and strengthening of the core muscles serve as the cornerstone of a stable, efficient, and resilient body. Beyond the quest for a toned midsection, a strong core facilitates optimal posture, enhances functional movement, and amplifies athletic performance. It’s the key to not just physical prowess but also injury prevention and overall well-being, empowering us to move through life with strength, balance, and confidence
Prepared by
Xin Ni
Your Physio Connaught

